The Ganga River, one of the most sacred and significant rivers in the world, flows through multiple countries, shaping the lives, culture, and environment of millions of people. Understanding which countries the Ganga River flows through is essential for anyone interested in geography, history, or environmental studies. In this article, we will explore the countries this mighty river traverses, its cultural significance, and its ecological importance.
The Ganga River, also known as the Ganges, is not just a geographical feature but a lifeline for millions of people. It plays a crucial role in agriculture, transportation, and industry, making it one of the most important rivers in Asia. The river's journey through different countries highlights its global importance and the challenges it faces.
This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of the Ganga River, focusing on the countries it flows through, its ecological significance, and the cultural impact it has on the regions it touches. Whether you are a student, researcher, or simply curious about the world's geography, this guide will offer valuable insights into the Ganga River's journey.
Read also:Inigo Montoya Portrayed By Unveiling The Iconic Character Behind The Princess Bride
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Ganga River
- Countries Through Which the Ganga River Flows
- Geography of the Ganga River
- Cultural Significance of the Ganga River
- Environmental Impact of the Ganga River
- Challenges Faced by the Ganga River
- Conservation Efforts for the Ganga River
- Historical Context of the Ganga River
- Key Statistics About the Ganga River
- Conclusion
Introduction to the Ganga River
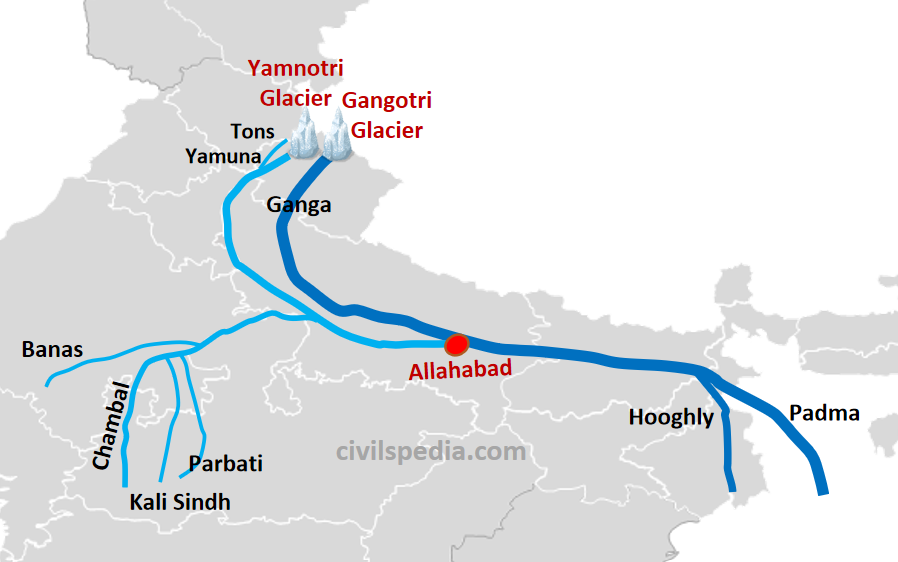
The Ganga River, originating in the Gangotri Glacier in the Indian Himalayas, is one of the longest rivers in Asia. Stretching over 2,525 kilometers, it plays a pivotal role in the lives of millions of people who depend on it for water, agriculture, and transportation. The river's basin covers an area of approximately 1 million square kilometers, making it one of the largest river basins in the world.
Key Features of the Ganga River
- Originates in the Gangotri Glacier in the Indian Himalayas.
- Flows through India and Bangladesh before emptying into the Bay of Bengal.
- Supports a population of over 400 million people in its basin.
The Ganga River is not just a source of water but also a symbol of spiritual and cultural heritage. It is revered by Hindus as a goddess and plays a central role in religious ceremonies and traditions.
Countries Through Which the Ganga River Flows
The Ganga River primarily flows through two countries: India and Bangladesh. Its journey begins in the Indian Himalayas and continues through the plains of northern India before entering Bangladesh, where it merges with other rivers to form the largest delta in the world.
India
In India, the Ganga River is a lifeline for millions of people. It supports agriculture, industry, and transportation, making it one of the most important rivers in the country. The river flows through several states, including Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal, before crossing into Bangladesh.
Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, the Ganga River is known as the Padma River. It merges with the Brahmaputra and Meghna rivers to form the Sundarbans Delta, the largest delta in the world. The river plays a crucial role in the country's economy, supporting agriculture, fishing, and transportation.
Geography of the Ganga River
The Ganga River begins its journey in the Gangotri Glacier, located in the Indian Himalayas, at an elevation of about 7,100 meters. From there, it flows through the Himalayan foothills and enters the Gangetic Plain, one of the most fertile regions in the world. The river's course is characterized by its meandering path and numerous tributaries, which contribute to its vast basin.
Read also:Martha Scott Lawyer A Comprehensive Guide To Her Career Expertise And Legacy
Tributaries of the Ganga River
- Yamuna River
- Ghaghara River
- Gandaki River
- Kosi River
These tributaries contribute significantly to the river's volume and help sustain the ecosystems and communities along its banks.
Cultural Significance of the Ganga River
The Ganga River holds immense cultural and religious significance, particularly in Hinduism. It is considered a sacred river and is worshipped as the goddess Ganga. Millions of Hindus bathe in the river during religious festivals, believing that it washes away sins and grants salvation.
Religious Practices
- Kumbh Mela: A mass Hindu pilgrimage held every 12 years at the banks of the Ganga River.
- Ganga Aarti: A daily ritual performed to honor the river goddess.
The river's cultural importance extends beyond religion, influencing art, literature, and music in the regions it touches.
Environmental Impact of the Ganga River
The Ganga River supports a diverse range of ecosystems, from the Himalayan forests to the Sundarbans mangroves. However, the river faces significant environmental challenges, including pollution, deforestation, and climate change.
Pollution
Industrial waste, untreated sewage, and agricultural runoff are major sources of pollution in the Ganga River. This has led to a decline in water quality, affecting both human health and aquatic life.
Climate Change
Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns are affecting the river's flow and water availability. Glacial melt due to climate change poses a threat to the long-term sustainability of the river.
Challenges Faced by the Ganga River
Despite its importance, the Ganga River faces numerous challenges that threaten its health and sustainability. These challenges include pollution, over-extraction of water, and habitat destruction.
Pollution Control
Efforts to control pollution in the Ganga River have been ongoing for decades. The Indian government has launched several initiatives, such as the Namami Gange Programme, aimed at cleaning and rejuvenating the river.
Water Management
Effective water management is crucial for ensuring the river's sustainability. This includes regulating water usage, improving wastewater treatment, and promoting conservation practices.
Conservation Efforts for the Ganga River
Conservation efforts for the Ganga River focus on restoring its ecological health and preserving its cultural significance. These efforts involve collaboration between governments, NGOs, and local communities.
Community Participation
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is essential for the success of these initiatives. Programs that educate and empower communities to protect the river have shown promising results.
Technological Innovations
Advancements in technology, such as wastewater treatment plants and monitoring systems, are being used to address the challenges facing the Ganga River. These innovations offer hope for a cleaner and healthier river in the future.
Historical Context of the Ganga River
The Ganga River has played a central role in the history of South Asia. It has been a source of inspiration for poets, artists, and philosophers and has witnessed the rise and fall of empires throughout history.
Ancient Civilizations
The Indus Valley Civilization and the Vedic civilization both flourished along the banks of the Ganga River. The river's fertile plains provided ideal conditions for agriculture, supporting the growth of these ancient civilizations.
Modern Era
In modern times, the Ganga River continues to be a vital resource for India and Bangladesh. Its importance in agriculture, industry, and transportation makes it a critical component of the region's economy.
Key Statistics About the Ganga River
Here are some key statistics about the Ganga River:
- Length: 2,525 kilometers
- Basin Area: Approximately 1 million square kilometers
- Population Supported: Over 400 million people
- Tributaries: Over 40 major tributaries
These statistics highlight the river's immense importance and the challenges it faces in sustaining such a large population.
Conclusion
The Ganga River flows through India and Bangladesh, supporting millions of people and playing a crucial role in the region's economy, culture, and environment. Despite the challenges it faces, efforts to conserve and rejuvenate the river offer hope for its future.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences about the Ganga River in the comments section below. Your feedback helps us improve and provide more valuable content. Don't forget to explore other articles on our site for more insights into geography, culture, and the environment.