Understanding the distinction between ethnicity and race is crucial in today's diverse world. Many people use these terms interchangeably, but they carry distinct meanings that affect how we identify ourselves and others. As societies grow more interconnected, grasping these concepts becomes increasingly important for fostering inclusivity and respect.
Race and ethnicity are fundamental aspects of identity, but they differ significantly in their definitions and implications. This article aims to clarify these differences, providing a deeper understanding of both concepts and their roles in shaping cultural and social dynamics.
By exploring the nuances of ethnicity and race, we can better appreciate the diversity of human experiences and build more equitable communities. Let's delve into the details to uncover the distinctions and connections between these two vital elements of identity.
Read also:April 21st Zodiac Sign Unveiling The Mystical Traits Of Taurus
Defining Ethnicity and Race
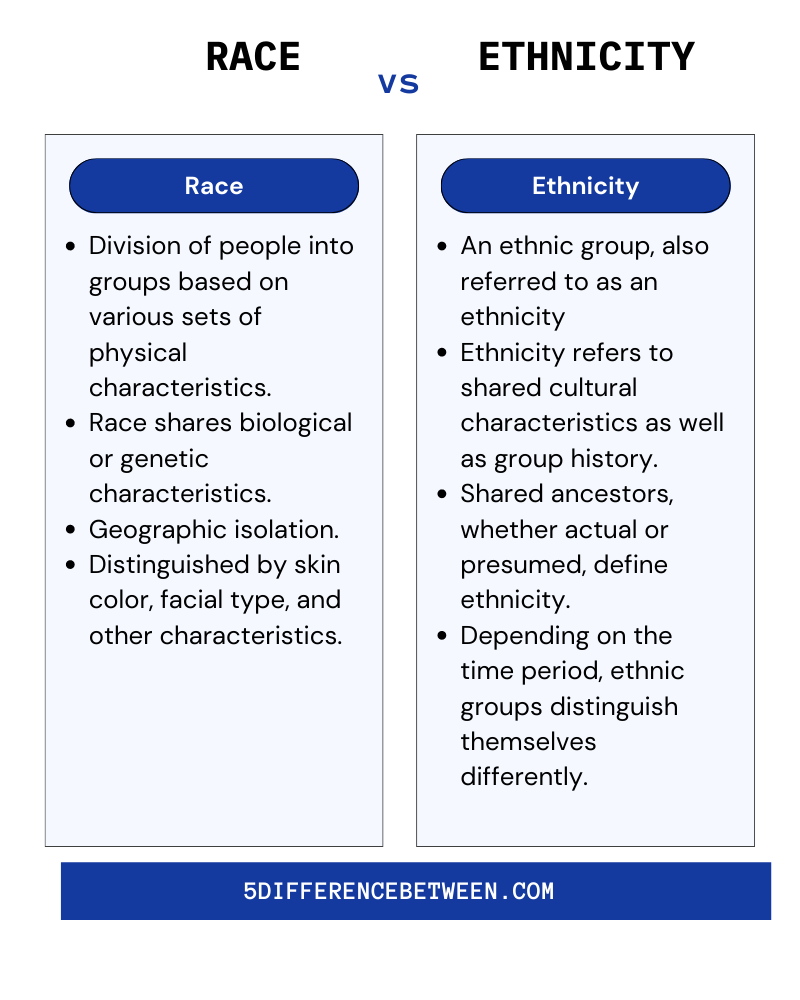
Before we examine the differences, it's essential to define both terms clearly. Ethnicity refers to a shared cultural heritage, including language, traditions, religion, and ancestry. On the other hand, race is a classification based on physical characteristics, such as skin color, facial features, and geographical origin.
Key Characteristics of Ethnicity
- Cultural practices and traditions
- Shared language and dialects
- Religious beliefs and customs
- Historical and ancestral connections
Key Characteristics of Race
- Physical traits like skin color and hair texture
- Biological and genetic factors
- Geographical ancestry
- Socially constructed categories
Historical Context of Ethnicity and Race
The concepts of ethnicity and race have evolved significantly over time. Historically, race was used to justify social hierarchies and inequalities, particularly during colonial and imperial eras. Meanwhile, ethnicity has been a way for communities to preserve their unique cultural identities amidst external influences.
How Race Became a Social Construct
Research shows that race is a relatively recent concept, emerging during the 17th and 18th centuries. According to the American Anthropological Association, race was primarily used to categorize people based on perceived physical differences. However, modern science has demonstrated that these distinctions lack biological validity.
The Evolution of Ethnic Identity
Ethnicity, on the other hand, has deeper historical roots, often tied to specific regions and communities. Over time, globalization and migration have led to the blending and redefining of ethnic identities. Today, many people identify with multiple ethnicities, reflecting the complexity of modern identity.
Key Differences Between Ethnicity and Race
The distinction between ethnicity and race lies in their focus areas. While ethnicity emphasizes cultural and social factors, race centers on physical and biological traits. This difference affects how individuals and societies perceive and interact with each other.
Cultural vs. Biological Factors
- Ethnicity: Cultural practices, language, and traditions
- Race: Physical characteristics and geographical ancestry
Flexibility and Fluidity
Ethnic identity can change over time, influenced by factors like migration, marriage, and cultural assimilation. Race, however, tends to remain more static, as it is based on inherited physical traits. This flexibility in ethnic identity allows for greater adaptability and inclusivity.
Read also:Harry Enten Height A Comprehensive Look At The Renowned Political Analyst
Social Implications of Ethnicity and Race
Understanding the differences between ethnicity and race is vital for addressing social issues like discrimination and inequality. Misunderstandings about these concepts can lead to harmful stereotypes and prejudice, affecting individuals and communities.
Impact on Identity Formation
Both ethnicity and race play significant roles in shaping personal and group identities. Ethnic identity often provides a sense of belonging and community, while racial identity can influence how individuals are perceived and treated by society. Recognizing these dual influences helps foster a more nuanced understanding of identity.
Addressing Stereotypes and Prejudice
Education and awareness are key to combating stereotypes and prejudice related to ethnicity and race. By promoting accurate information and encouraging open dialogue, we can work towards a more inclusive and equitable society. Organizations like UNESCO and the United Nations actively support initiatives to combat racial discrimination and promote cultural diversity.
Scientific Perspectives on Ethnicity and Race
Modern science has shed light on the biological and social aspects of ethnicity and race. Genetic research shows that human diversity is far more complex than traditional racial categories suggest. Meanwhile, sociological studies highlight the importance of cultural identity in shaping individual and group experiences.
Genetic Diversity and Race
Studies conducted by the Human Genome Project reveal that there is more genetic variation within so-called racial groups than between them. This challenges the traditional notion of race as a biologically distinct category and supports the view that race is primarily a social construct.
Cultural Identity and Ethnicity
Sociologists emphasize the importance of cultural identity in shaping ethnic affiliations. Factors like language, religion, and historical ties contribute to a shared sense of identity among ethnic groups. Understanding these elements helps explain why ethnic identity remains a powerful force in today's globalized world.
Legal and Policy Considerations
Governments and institutions often use race and ethnicity as categories for data collection and policy-making. These classifications can have significant implications for issues like affirmative action, voting rights, and healthcare access. Ensuring accurate and respectful use of these terms is crucial for effective policymaking.
Race in Government Data
In the United States, the Census Bureau collects data on race and ethnicity to inform policy decisions. The categories used have evolved over time to reflect changing social understandings of these concepts. However, challenges remain in accurately capturing the complexity of identity through standardized classifications.
Ethnicity in International Contexts
Global organizations like the World Health Organization and the International Labour Organization consider ethnicity in their work to address health disparities and labor rights. Recognizing the importance of cultural identity in these contexts helps ensure that policies are inclusive and effective across diverse populations.
Personal and Community Perspectives
For many individuals and communities, ethnicity and race are deeply personal aspects of identity. Personal experiences and community traditions shape how people understand and express these identities. Respecting these diverse perspectives is essential for building inclusive societies.
Self-Identification and Pride
Many people take pride in their ethnic and racial identities, viewing them as integral parts of their heritage and self-expression. Celebrating these identities through cultural events, language preservation, and artistic expression helps maintain their vitality and relevance in modern times.
Challenges and Resilience
Communities often face challenges related to discrimination and marginalization based on ethnicity and race. However, resilience and solidarity among these groups demonstrate the power of cultural identity in overcoming adversity. Supporting these communities through advocacy and allyship is crucial for promoting social justice.
Education and Awareness
Increasing education and awareness about the differences between ethnicity and race is vital for fostering understanding and respect. Schools, workplaces, and community organizations play key roles in promoting accurate information and encouraging open conversations about these topics.
Teaching About Identity
Curricula that include lessons on ethnicity and race help students develop a deeper understanding of these concepts. By incorporating diverse perspectives and histories, educators can prepare students to navigate an increasingly interconnected world.
Encouraging Dialogue
Creating safe spaces for discussions about ethnicity and race allows individuals to share their experiences and learn from others. Workshops, forums, and support groups provide opportunities for meaningful dialogue and mutual understanding.
Future Directions and Opportunities
As societies continue to evolve, so too will our understanding of ethnicity and race. Embracing the complexity of these concepts offers opportunities for greater inclusivity and equity. By continuing to learn and grow, we can build a more just and compassionate world.
Innovative Approaches
Technological advancements and social media platforms provide new ways to explore and celebrate cultural diversity. Virtual events, online communities, and digital storytelling offer innovative avenues for sharing and preserving ethnic and racial identities.
Policy and Advocacy
Ongoing efforts to reform policies and advocate for equity in areas like education, healthcare, and employment will help address longstanding disparities related to ethnicity and race. Supporting these initiatives is essential for creating lasting change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between ethnicity and race is crucial for promoting inclusivity and respect in our diverse world. By recognizing the cultural and social dimensions of ethnicity alongside the biological and historical aspects of race, we can better appreciate the richness of human identity.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Engaging in open and respectful dialogue helps us all grow and learn. For more insights on related topics, explore our other articles and resources. Together, we can continue to build a more informed and inclusive society.
Table of Contents
- Defining Ethnicity and Race
- Historical Context of Ethnicity and Race
- Key Differences Between Ethnicity and Race
- Social Implications of Ethnicity and Race
- Scientific Perspectives on Ethnicity and Race
- Legal and Policy Considerations
- Personal and Community Perspectives
- Education and Awareness
- Future Directions and Opportunities
- Conclusion