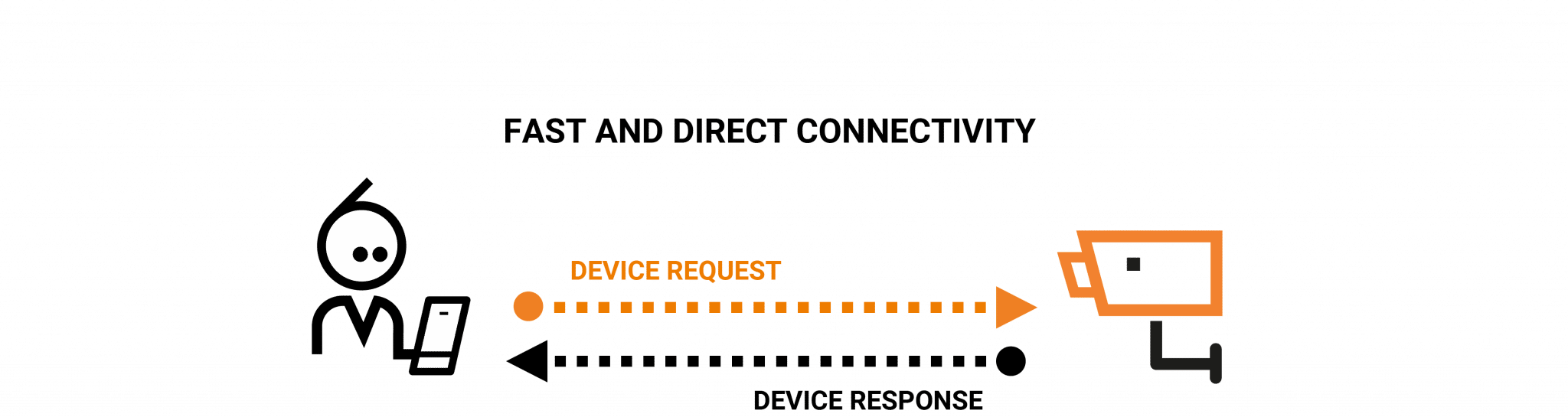
In today's interconnected world, the Internet of Things (IoT) plays a crucial role in transforming how devices interact and share data. One of the most fascinating concepts within IoT is Peer-to-Peer (P2P) networking. P2P in IoT enables devices to communicate directly without relying heavily on centralized servers, improving efficiency and scalability. Understanding this technology is essential for anyone looking to dive deeper into the world of IoT.
IoT continues to evolve, connecting billions of devices globally, and P2P technology offers a unique solution to some of the challenges faced by traditional IoT systems. By decentralizing communication, P2P networks reduce latency, enhance security, and increase reliability. This article aims to provide an in-depth explanation of P2P in IoT, including practical examples and its benefits.
As we explore this topic further, we'll discuss how P2P works in IoT, its advantages, and potential challenges. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a developer, or a business owner, understanding P2P in IoT can help you leverage its full potential. Let’s dive in!
Read also:Judi Dench Young A Comprehensive Look Into The Early Life And Career Of The Legendary Actress
Table of Contents
- What is P2P in IoT?
- How Does P2P Work in IoT?
- Examples of P2P in IoT
- Advantages of P2P in IoT
- Challenges of P2P in IoT
- P2P vs Traditional IoT
- Security in P2P IoT
- Scalability of P2P Networks
- Use Cases of P2P in IoT
- Future of P2P in IoT
- Conclusion
What is P2P in IoT?
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) in IoT refers to a decentralized networking model where devices communicate directly with each other without relying on a central server or authority. This approach is gaining popularity due to its ability to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve scalability. In a P2P IoT network, each device acts as both a client and a server, enabling seamless data exchange.
P2P technology is not new; it has been used for file-sharing platforms like BitTorrent and decentralized applications. However, its application in IoT brings new dimensions to device connectivity and interaction. The concept allows devices to operate independently, reducing reliance on cloud-based infrastructure and improving overall performance.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global IoT market is expected to grow significantly, with P2P networking playing a pivotal role in this expansion. By understanding the fundamentals of P2P in IoT, businesses can harness its potential to create innovative solutions and enhance user experiences.
How Does P2P Work in IoT?
P2P networks in IoT operate on the principle of decentralization, where devices connect directly to share resources and data. Unlike traditional client-server models, P2P eliminates the need for a central authority, enabling devices to communicate more efficiently. This section explores the mechanics of P2P in IoT:
Device Discovery
Before devices can communicate, they must first discover each other. In P2P IoT, devices use protocols such as Bluetooth, Zigbee, or Wi-Fi Direct to identify nearby peers. This process ensures that only authorized devices can join the network, enhancing security.
Data Exchange
Once devices are connected, they can exchange data directly. This process involves sending and receiving information in the form of packets. P2P networks often use encryption to secure data transmission, ensuring privacy and integrity.
Read also:Rob Dyrdek Family An Indepth Look Into The Life Of The Skateboarding Legend And His Loved Ones
Resource Sharing
P2P in IoT allows devices to share resources such as processing power, storage, and bandwidth. This capability is particularly useful in scenarios where devices need to collaborate to perform complex tasks, such as analyzing sensor data or executing machine learning algorithms.
Examples of P2P in IoT
To better understand the application of P2P in IoT, let’s look at some practical examples:
- Smart Home Automation: Devices like smart thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras can communicate directly, enabling seamless automation without relying on cloud servers.
- Industrial IoT: In manufacturing plants, sensors and machines can form a P2P network to monitor and optimize production processes in real-time.
- Healthcare IoT: Wearable devices and medical equipment can exchange data directly, providing doctors with real-time patient information for faster decision-making.
Advantages of P2P in IoT
P2P networking offers several advantages in IoT applications:
Efficiency
By eliminating the need for a central server, P2P networks reduce latency and improve response times. Devices can communicate directly, enabling faster data exchange and real-time interactions.
Scalability
P2P networks can scale easily as more devices join the network. Since each device contributes to the network's resources, the system can handle increased loads without degrading performance.
Reliability
Decentralized networks are less prone to single points of failure. If one device fails, others can continue functioning, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
Challenges of P2P in IoT
Despite its advantages, P2P in IoT also presents some challenges:
Security
Decentralized networks can be more vulnerable to cyberattacks, as there is no central authority to enforce security policies. Developers must implement robust encryption and authentication mechanisms to protect devices and data.
Complexity
Designing and maintaining P2P networks can be more complex than traditional architectures. Developers need to consider factors such as device discovery, data synchronization, and fault tolerance.
Interoperability
Different devices may use varying protocols and standards, making it challenging to ensure seamless communication. Standardization efforts are essential to address this issue.
P2P vs Traditional IoT
When comparing P2P with traditional IoT architectures, the differences become apparent:
Centralized vs Decentralized
Traditional IoT relies on centralized servers to manage device communication, while P2P eliminates this dependency, enabling direct device-to-device interaction.
Cost
P2P networks reduce costs associated with maintaining central servers and infrastructure. However, they may require additional resources for security and management.
Performance
P2P networks offer superior performance in terms of speed and reliability, especially in scenarios where real-time data exchange is critical.
Security in P2P IoT
Security is a top priority in P2P IoT networks. Developers must implement robust measures to protect devices and data from unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Some best practices include:
- Using encryption protocols such as AES and TLS to secure data transmission.
- Implementing strong authentication mechanisms to ensure only authorized devices can join the network.
- Regularly updating firmware and software to patch vulnerabilities.
Scalability of P2P Networks
P2P networks are inherently scalable, as each device contributes to the network's resources. This characteristic makes them ideal for large-scale IoT deployments. However, developers must carefully design the network architecture to ensure optimal performance as the number of devices grows.
Use Cases of P2P in IoT
P2P technology has a wide range of applications in IoT. Some notable use cases include:
Smart Cities
P2P networks can connect various urban systems, such as traffic management, public transportation, and energy distribution, enabling efficient resource utilization and improved quality of life for citizens.
Agriculture
In precision agriculture, P2P IoT can enable sensors and drones to work together, collecting and analyzing data to optimize crop yield and reduce resource consumption.
Environmental Monitoring
P2P networks can be used to monitor environmental conditions, such as air quality, water levels, and temperature, providing valuable insights for conservation efforts.
Future of P2P in IoT
The future of P2P in IoT looks promising, with advancements in technology driving its adoption. Emerging trends such as edge computing, blockchain, and artificial intelligence are expected to enhance P2P capabilities, enabling more sophisticated applications and use cases.
As IoT continues to expand, P2P networks will play a vital role in creating interconnected ecosystems that deliver value to businesses and consumers alike. Staying updated with the latest developments in this field is crucial for anyone looking to capitalize on its potential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, P2P in IoT represents a groundbreaking approach to device connectivity and interaction. By enabling direct communication between devices, P2P networks offer numerous advantages, including improved efficiency, scalability, and reliability. However, challenges such as security and complexity must be addressed to fully realize its potential.
We encourage readers to explore the possibilities of P2P in IoT and consider how it can benefit their projects or businesses. Please leave your thoughts and questions in the comments section below and share this article with others who may find it useful. For more insights into IoT and related technologies, explore our other articles on the site.