Exploring the differences between ethnicity and race is crucial in understanding cultural diversity and identity in today's globalized world. These concepts often overlap, but they are distinct in their meanings and implications. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will uncover the nuances that set them apart and why it matters.
Race and ethnicity are terms frequently used interchangeably, but they carry different meanings that shape how we perceive ourselves and others. Understanding these distinctions can help foster better communication and reduce misunderstandings in multicultural environments. This article aims to clarify the differences between ethnicity and race while exploring their social, historical, and cultural significance.
Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply someone interested in cultural studies, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the differences between ethnicity and race. Let's embark on this journey to unravel the complexities of identity and diversity.
Read also:Masiela Lusha A Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- Defining the Terms: Ethnicity and Race
- Historical Context of Ethnicity and Race
- Biological vs. Cultural: Key Differences
- Ethnicity Explained
- Race Explained
- Overlapping Concepts: Where Ethnicity Meets Race
- Cultural Significance of Ethnicity and Race
- Common Misconceptions About Ethnicity and Race
- Conclusion: Why Understanding Matters
Defining the Terms: Ethnicity and Race
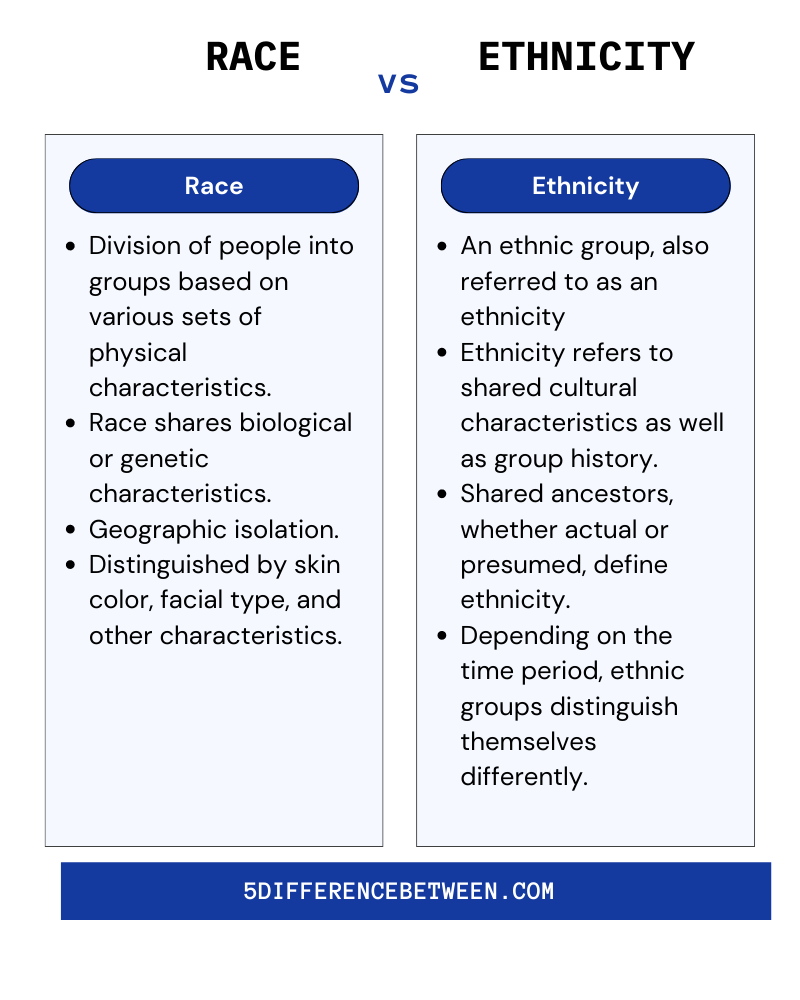
Before diving into the differences between ethnicity and race, it is essential to define each term clearly. Ethnicity refers to a shared cultural heritage, including language, traditions, religion, and ancestry. On the other hand, race is based on physical characteristics, such as skin color, facial features, and genetic makeup. While ethnicity is a social construct rooted in culture, race is often associated with biological differences.
It is important to note that both ethnicity and race are fluid concepts that evolve over time. They are influenced by historical, political, and societal factors, making them complex and multifaceted.
Understanding the distinctions between these terms is vital for promoting inclusivity and combating stereotypes. By recognizing the unique aspects of ethnicity and race, we can appreciate the richness of human diversity.
Historical Context of Ethnicity and Race
The history of ethnicity and race is deeply intertwined with colonization, migration, and globalization. During the colonial era, race was used as a tool for categorizing and controlling populations. European colonizers imposed racial hierarchies that perpetuated inequality and discrimination.
In contrast, ethnicity emerged as a way for communities to preserve their cultural identities in the face of external pressures. Immigrants and indigenous groups often relied on shared ethnic bonds to maintain their traditions and resist assimilation.
Today, the legacy of historical discrimination continues to shape how we perceive ethnicity and race. Efforts to address these issues involve promoting education, awareness, and dialogue across diverse communities.
Read also:April 21st Zodiac Sign Unveiling The Mystical Traits Of Taurus
Biological vs. Cultural: Key Differences
One of the primary distinctions between ethnicity and race lies in their biological and cultural dimensions. Race is often tied to physical traits that are genetically inherited, such as skin color and hair texture. These characteristics are used to classify individuals into broad racial categories.
Ethnicity, on the other hand, is rooted in cultural practices and shared experiences. It encompasses language, religion, cuisine, and other aspects of daily life that define a group's identity. While race focuses on biological differences, ethnicity emphasizes the social and cultural dimensions of identity.
It is worth noting that both race and ethnicity are social constructs influenced by societal norms and values. They are not fixed or immutable but are shaped by historical and cultural contexts.
Ethnicity Explained
Ethnicity is a complex concept that reflects the cultural heritage and identity of a group. It is defined by shared characteristics such as language, traditions, religion, and ancestry. Unlike race, ethnicity is not based on physical traits but on cultural and social affiliations.
Characteristics of Ethnicity
Ethnic groups are typically identified by the following characteristics:
- Shared language and dialects
- Cultural traditions, such as festivals and rituals
- Religious beliefs and practices
- Common ancestry or historical origins
- Distinct cuisine and culinary practices
These features create a sense of belonging and unity among members of an ethnic group, fostering a strong cultural identity.
Examples of Ethnic Groups
Some well-known ethnic groups around the world include:
- Hispanic/Latino
- Chinese
- Indian
- African American
- Arab
Each of these groups has its own unique cultural traditions and practices that distinguish them from others. Understanding the diversity within ethnic groups is essential for promoting mutual respect and understanding.
Race Explained
Race is a classification system based on physical characteristics such as skin color, facial features, and genetic makeup. It is often used to categorize individuals into broad groups, such as Caucasian, African, Asian, and Indigenous. While race is rooted in biology, it is also a social construct influenced by historical and cultural factors.
Classification of Race
Racial categories vary across different regions and cultures. In the United States, for example, the U.S. Census Bureau recognizes five major racial groups:
- White
- Black or African American
- Asian
- Native American or Alaska Native
- Pacific Islander
These classifications are used for statistical purposes and to track demographic trends. However, they are not without controversy, as they oversimplify the complexity of human identity.
Social Implications of Race
Race has significant social implications, influencing how individuals are perceived and treated in society. Racial stereotypes and biases can lead to discrimination, inequality, and social injustice. Efforts to address these issues involve promoting education, awareness, and policy changes that support racial equality.
Understanding the social dimensions of race is crucial for fostering inclusivity and combating systemic racism. By recognizing the impact of race on individuals and communities, we can work towards a more equitable society.
Overlapping Concepts: Where Ethnicity Meets Race
While ethnicity and race are distinct concepts, they often overlap in meaningful ways. Many ethnic groups are also racialized, meaning they are categorized based on physical characteristics as well as cultural identity. For example, African Americans may identify as both a racial and ethnic group, sharing a common ancestry and cultural heritage.
This intersectionality highlights the complexity of identity and the need for nuanced understanding. Recognizing the interplay between ethnicity and race can help us appreciate the diversity of human experience and promote greater empathy and understanding.
Cultural Significance of Ethnicity and Race
Ethnicity and race play a vital role in shaping cultural identity and expression. They influence art, music, literature, and other forms of creative expression that reflect the values and traditions of a community. By celebrating the cultural contributions of diverse groups, we enrich our collective understanding of humanity.
Moreover, understanding the cultural significance of ethnicity and race can help bridge divides and foster cross-cultural communication. It encourages us to embrace differences while recognizing our shared humanity.
Common Misconceptions About Ethnicity and Race
There are several misconceptions surrounding ethnicity and race that can lead to confusion and misunderstanding. One common myth is that race is a purely biological concept, ignoring its social and cultural dimensions. Another misconception is that ethnicity is fixed and unchanging, failing to account for the fluidity of cultural identity.
Addressing these misconceptions involves promoting education and awareness about the complexities of identity. By challenging stereotypes and biases, we can create a more inclusive and informed society.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Matters
In conclusion, understanding the differences between ethnicity and race is essential for promoting cultural awareness and inclusivity. While ethnicity focuses on cultural heritage and identity, race is based on physical characteristics and genetic makeup. Both concepts are shaped by historical, social, and cultural factors that influence how we perceive ourselves and others.
By recognizing the distinctions and intersections between ethnicity and race, we can foster greater empathy and understanding across diverse communities. We encourage readers to engage in meaningful conversations about identity and diversity, leaving comments or sharing this article to continue the dialogue.
For further reading, explore related topics such as cultural identity, globalization, and social justice. Together, we can build a more equitable and harmonious world.