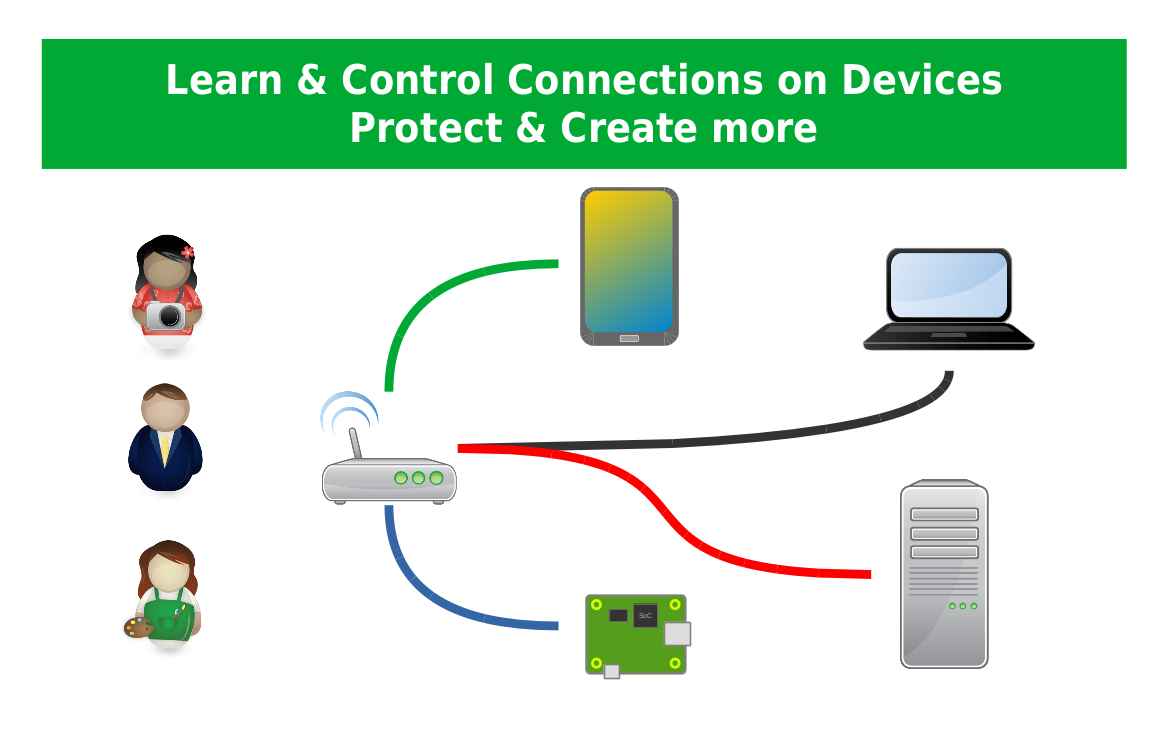
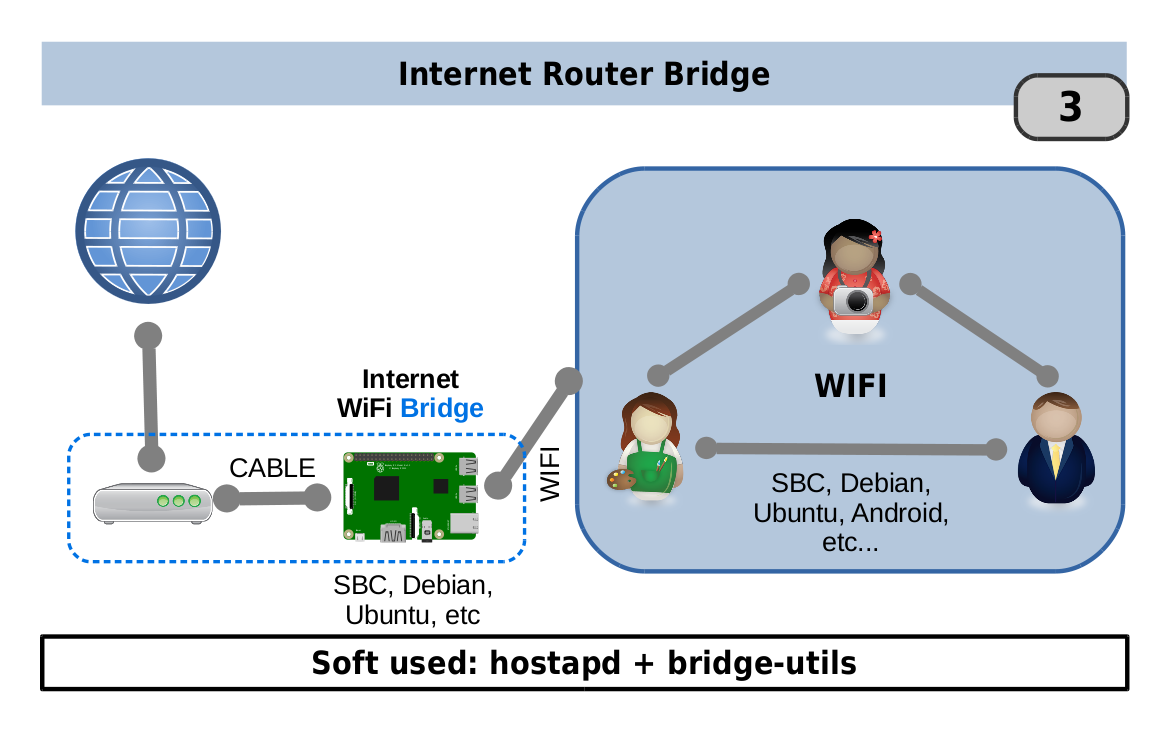
Setting up a Raspberry Pi P2P network has become a popular choice for tech enthusiasts and professionals alike who want to explore decentralized networking solutions. Whether you're looking to share files, create a secure communication channel, or experiment with peer-to-peer technology, Raspberry Pi offers an affordable and versatile platform to achieve these goals. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of building a Raspberry Pi P2P network, providing you with step-by-step instructions and expert insights.
Raspberry Pi has revolutionized the way we approach computing and networking. With its compact size and impressive capabilities, it has become the go-to device for hobbyists, educators, and professionals. By leveraging Raspberry Pi's power, you can create a P2P network that enhances collaboration, data sharing, and connectivity.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the essential components of a Raspberry Pi P2P network, including setup procedures, security considerations, and optimization techniques. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to build and manage your own decentralized network using Raspberry Pi.
Read also:Elizabeth Short Autopsy Photos A Deep Dive Into The Legacy Of The Black Dahlia
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Raspberry Pi P2P Network
- Required Hardware for Raspberry Pi P2P Network
- Software Setup and Configuration
- Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up the Network
- Securing Your Raspberry Pi P2P Network
- Optimizing Performance for Maximum Efficiency
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
- Applications of Raspberry Pi P2P Networks
- Raspberry Pi P2P vs Traditional Networks
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Raspberry Pi P2P Network
Understanding P2P Networking
A Raspberry Pi P2P network operates on the principle of peer-to-peer communication, where devices directly interact with each other without relying on centralized servers. This decentralized approach offers numerous advantages, including enhanced security, improved reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Why Choose Raspberry Pi?
Raspberry Pi stands out as an ideal platform for building a P2P network due to its affordability, energy efficiency, and versatility. It supports a wide range of operating systems and programming languages, making it suitable for various applications, from file sharing to IoT projects.
Benefits of a Raspberry Pi P2P Network
- Cost-effective solution for networking needs
- Improved data privacy and security
- Scalability for small to large-scale projects
- Customizability to fit specific requirements
Required Hardware for Raspberry Pi P2P Network
Before setting up your Raspberry Pi P2P network, it's essential to gather the necessary hardware components. Below is a list of items you will need:
- Raspberry Pi board (Model 4B recommended)
- MicroSD card with at least 16GB capacity
- Power adapter compatible with Raspberry Pi
- Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi dongle for connectivity
- HDMI monitor and keyboard (optional)
Software Setup and Configuration
Choosing the Right Operating System
For a Raspberry Pi P2P network, it is recommended to use lightweight operating systems such as Raspbian or Ubuntu Server. These OS options provide the necessary tools and utilities to configure and manage your network efficiently.
Installing Required Software
Once the operating system is installed, you will need to install additional software packages to enable P2P functionality. Popular choices include:
- Transmission for torrenting and file sharing
- OpenSSH for secure remote access
- Avahi for zero-configuration networking
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up the Network
Step 1: Initial Setup
Begin by connecting your Raspberry Pi to a monitor and keyboard. Insert the microSD card with the pre-installed operating system and power on the device. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the initial setup process.
Read also:Are Matt And Frannie Still Together Exploring Their Relationship Status
Step 2: Configuring Network Settings
Access the network configuration file using the terminal and modify the settings to enable peer-to-peer communication. Use the following command:
sudo nano /etc/dhcpcd.conf
Add the following lines to configure a static IP address:
interface eth0
static ip_address=192.168.1.100/24
static routers=192.168.1.1
static domain_name_servers=8.8.8.8
Step 3: Enabling P2P Services
Install and configure P2P services such as BitTorrent Sync or Syncthing to facilitate file sharing between Raspberry Pi devices. These tools provide a user-friendly interface and robust security features.
Securing Your Raspberry Pi P2P Network
Implementing Strong Passwords
Ensure all devices in your Raspberry Pi P2P network are protected with strong, unique passwords. Avoid using default credentials and consider enabling two-factor authentication for added security.
Using Encryption Protocols
Encrypt your network traffic using protocols such as SSH or SSL to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. This is especially important when sharing sensitive information over the network.
Regular Updates and Backups
Keep your Raspberry Pi and all connected devices up to date with the latest software patches and security updates. Regularly back up important data to prevent loss in case of system failures.
Optimizing Performance for Maximum Efficiency
Optimizing Network Bandwidth
Monitor and adjust network bandwidth settings to ensure optimal performance. Use tools like iftop or nload to analyze traffic patterns and identify potential bottlenecks.
Enhancing Storage Capacity
Consider adding external storage devices, such as USB drives or network-attached storage (NAS), to expand the storage capacity of your Raspberry Pi P2P network. This will allow you to store and share larger files without compromising performance.
Tuning System Settings
Adjust system settings to prioritize resource allocation for P2P applications. Modify parameters such as CPU and memory usage to maximize efficiency and responsiveness.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Connection Problems
If you encounter connection issues, verify that all devices are properly connected and configured. Check network settings and restart the Raspberry Pi if necessary.
Slow Transfer Speeds
Slow transfer speeds can be caused by insufficient bandwidth or suboptimal network configuration. Use diagnostic tools to identify and resolve the underlying issue.
Software Compatibility Issues
Ensure all software components are compatible with your Raspberry Pi's operating system and hardware specifications. Consult official documentation and community forums for guidance.
Applications of Raspberry Pi P2P Networks
File Sharing and Collaboration
A Raspberry Pi P2P network is ideal for sharing files and collaborating on projects. It allows multiple users to access and modify shared resources simultaneously, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
IoT Device Networking
By integrating IoT devices into your Raspberry Pi P2P network, you can create a smart home ecosystem that enhances convenience and automation. Control devices such as smart lights, thermostats, and security systems through your decentralized network.
Educational Purposes
Raspberry Pi P2P networks provide an excellent platform for learning and experimentation. Students and educators can explore networking concepts, programming, and system administration in a hands-on environment.
Raspberry Pi P2P vs Traditional Networks
Cost-Effectiveness
Raspberry Pi P2P networks offer a more cost-effective solution compared to traditional networks, as they eliminate the need for expensive hardware and software licenses.
Scalability and Flexibility
While traditional networks may require significant infrastructure changes to scale, Raspberry Pi P2P networks can easily accommodate additional devices and applications without incurring substantial costs.
Security Considerations
Both Raspberry Pi P2P and traditional networks require robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. However, P2P networks often provide enhanced privacy and control over shared resources.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, setting up a Raspberry Pi P2P network offers numerous benefits, including cost-effectiveness, scalability, and enhanced security. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a functional and efficient decentralized network tailored to your specific needs.
We encourage you to share your experiences and insights in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more information on Raspberry Pi projects and networking solutions. Together, let's build a better-connected future!
Data Source: Raspberry Pi Foundation, Debian Project, Ubuntu