Learning how to insert a tampon is an essential skill for women and individuals who menstruate. It’s a topic that can often feel intimidating, but with the right information, it becomes much simpler and more manageable. Tampons are a convenient and effective way to manage your period, and understanding the process can enhance your confidence and comfort during menstruation.
Many people have questions about the process of inserting a tampon, especially if they are new to it. Whether you’re a teenager just starting to explore your options or an adult looking for a more comfortable solution, this guide will walk you through every step. From understanding the anatomy to troubleshooting common issues, we’ve got you covered.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to insert a tampon safely and effectively. We’ll also address common concerns, such as pain, discomfort, and hygiene. Let’s dive in and demystify the process together!
Read also:Unveiling The Truth About Boly4uin A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Understanding Your Anatomy
- Types of Tampons
- Step-by-Step Guide on How to Insert a Tampon
- Common Issues and How to Solve Them
- Tips for First-Time Users
- Maintaining Hygiene
- Benefits of Using Tampons
- Risks and Precautions
- Alternatives to Tampons
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Your Anatomy
Before we dive into the specifics of inserting a tampon, it’s important to understand the female anatomy. The vagina is a muscular canal that connects the uterus to the outside of the body. It is designed to accommodate a variety of objects, including tampons, menstrual cups, and even babies during childbirth. Contrary to popular belief, the vagina is not a fragile structure; it is elastic and capable of expanding and contracting as needed.
Key Parts of the Female Anatomy
Here are the key parts of the female anatomy that are relevant when inserting a tampon:
- Labia: The outer and inner folds of skin that protect the vaginal opening.
- Vaginal Opening: The entrance to the vagina, where the tampon will be inserted.
- Urethra: A small opening above the vaginal opening that allows urine to exit the body.
- Hymen: A thin membrane that partially covers the vaginal opening in some individuals. It can stretch or tear without causing harm.
Understanding these parts will help you feel more confident when inserting a tampon. Remember, your body is designed to accommodate tampons, so there’s no need to worry about causing damage.
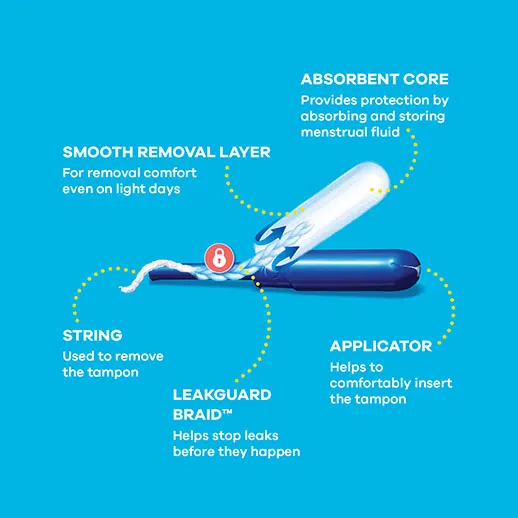
Types of Tampons
Not all tampons are created equal. There are various types of tampons available, each with its own features and benefits. Choosing the right tampon for your needs is crucial for comfort and effectiveness.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Tampon
Here are some factors to consider:
- Absorbency: Tampons come in different absorbency levels, such as light, regular, super, and super plus. Choose the absorbency level that matches your flow.
- Applicator Type: Some tampons come with applicators made of plastic or cardboard, while others are applicator-free. Applicator-free tampons are often more eco-friendly but may require a bit more practice.
- Material: Tampons can be made from cotton, rayon, or a blend of both. Look for tampons that are free from harmful chemicals and fragrances.
Experiment with different types of tampons to find the one that works best for you. Remember, comfort is key!
Read also:Why Did Joe Leave Impractical Jokers The Untold Story
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Insert a Tampon
Now that you understand your anatomy and the types of tampons available, let’s go through the step-by-step process of inserting a tampon.
Step 1: Choose the Right Environment
Find a comfortable and private place to insert your tampon. You can sit on the toilet, squat, or stand with one foot raised on the edge of the bathtub. The key is to relax and take your time.
Step 2: Unwrap the Tampon
Unwrap the tampon carefully, ensuring that the string is visible and the applicator (if applicable) is intact. If you’re using an applicator-free tampon, make sure your hands are clean and dry.
Step 3: Position the Tampon
Hold the tampon or applicator comfortably in your hand. If using an applicator, grip it at the middle, where the wider part meets the narrower part. If using an applicator-free tampon, pinch the tampon between your fingers.
Step 4: Insert the Tampon
Gently insert the tampon into your vagina, aiming it toward your lower back. Push it in until it feels comfortable and secure. If using an applicator, push the narrower part of the applicator into the wider part until the tampon is fully inserted.
Step 5: Remove the Applicator (If Applicable)
If you’re using an applicator, twist or pull it gently to remove it. Leave the string hanging outside your body for easy removal later.
That’s it! You’ve successfully inserted a tampon. If it feels uncomfortable, try adjusting your position or inserting it again.
Common Issues and How to Solve Them
Even with proper guidance, some people may encounter issues when inserting a tampon. Here are some common problems and solutions:
Issue 1: Pain or Discomfort
Pain or discomfort during insertion can be caused by tension, incorrect positioning, or using a tampon with the wrong absorbency level. To solve this, try relaxing your muscles, adjusting your position, or switching to a lighter absorbency tampon.
Issue 2: Difficulty Inserting
If you’re having trouble inserting the tampon, ensure that you’re using the correct technique. Practice different positions and experiment with different types of tampons until you find one that feels right.
Issue 3: Tampon Not Staying in Place
If the tampon doesn’t stay in place, it may not be inserted far enough. Gently push it in further until it feels secure. If the problem persists, consider using a different type of tampon.
Tips for First-Time Users
For those who are new to tampons, here are some additional tips to make the process easier:
- Start with a light absorbency tampon to reduce discomfort.
- Use a tampon with an applicator if you’re unsure about inserting it without one.
- Practice inserting the tampon in front of a mirror to get a better understanding of your anatomy.
- Don’t rush the process—take your time and relax.
Remember, it’s normal to feel nervous at first, but with practice, inserting a tampon will become second nature.
Maintaining Hygiene
Proper hygiene is crucial when using tampons. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Change your tampon every 4 to 8 hours to prevent infections and maintain freshness.
- Wash your hands before and after inserting or removing a tampon.
- Dispose of used tampons properly by wrapping them in toilet paper or using a sanitary bin.
Following these hygiene practices will help you stay healthy and comfortable during your period.
Benefits of Using Tampons
Tampons offer several benefits over other menstrual products. Here are some of the advantages:
- Discreet: Tampons are small and easy to carry, making them perfect for on-the-go use.
- Comfortable: Once inserted correctly, tampons are virtually invisible and allow for unrestricted movement.
- Effective: Tampons can absorb more menstrual fluid than pads, making them ideal for heavy flows.
These benefits make tampons a popular choice for many individuals who menstruate.
Risks and Precautions
While tampons are generally safe to use, there are some risks to be aware of. The most significant risk is Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS), a rare but serious condition caused by bacterial infection. To reduce the risk of TSS:
- Change your tampon regularly, every 4 to 8 hours.
- Avoid using high-absorbency tampons unless necessary.
- Consider alternating tampons with pads or menstrual cups during your period.
By following these precautions, you can minimize the risks associated with tampon use.
Alternatives to Tampons
While tampons are a popular choice, there are other menstrual products available that may suit your needs better. Here are some alternatives:
- Menstrual Cups: Reusable silicone cups that collect menstrual fluid.
- Pads: Disposable or reusable pads that absorb menstrual fluid.
- Period Underwear: Specialized underwear designed to absorb menstrual flow.
Explore these options to find the product that works best for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can a tampon get lost inside me?
No, a tampon cannot get lost inside you. The vagina is a closed muscular canal, and the cervix at the top prevents anything from passing through. If you’re having trouble removing a tampon, relax and gently pull on the string.
Q: Can I swim with a tampon?
Yes, you can swim with a tampon. It will absorb water, but it won’t leak as long as it’s inserted correctly. Consider using a high-absorbency tampon if you’re swimming for an extended period.
Q: Can I sleep with a tampon?
Yes, you can sleep with a tampon, but it’s important to use the correct absorbency level and change it as soon as you wake up. Alternatively, consider using a pad or menstrual cup for overnight protection.
Conclusion
Learning how to insert a tampon is an important skill that can enhance your comfort and confidence during menstruation. By understanding your anatomy, choosing the right tampon, and following proper hygiene practices, you can make the process easier and more enjoyable. Remember to address any concerns or issues promptly and seek professional advice if needed.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. If you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with others who may benefit from it. For more information on menstrual health and related topics, explore our other articles on the site.