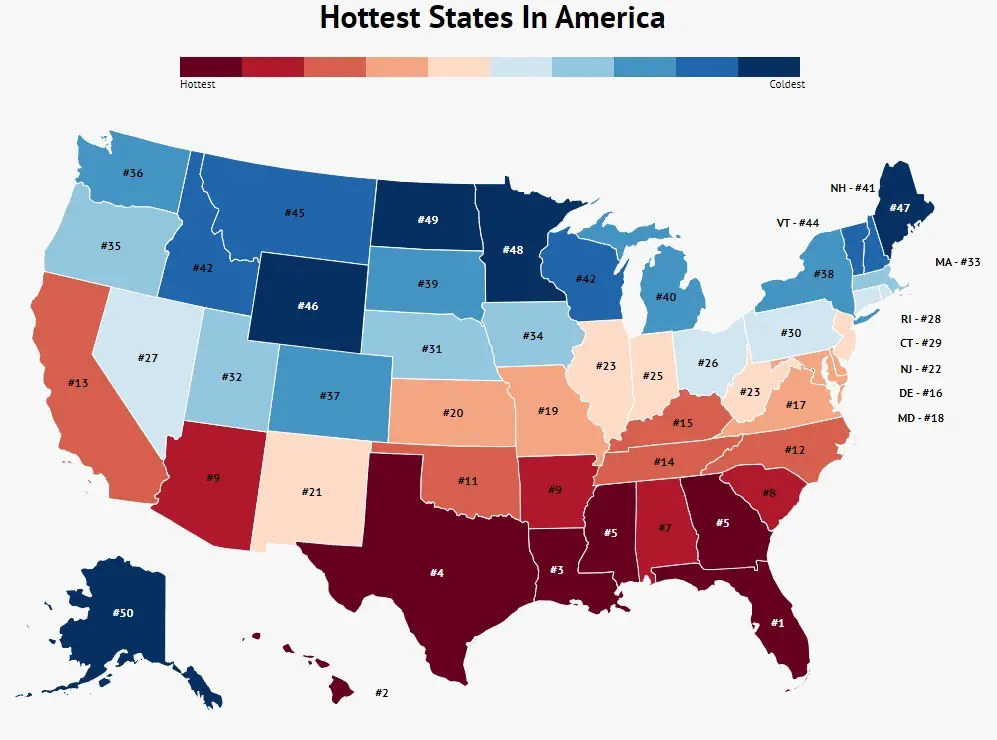
When it comes to the hottest state in the United States, many people think of scorching deserts and relentless sunshine. The state of Arizona often comes to mind, but what exactly makes it the hottest? Understanding the factors that contribute to extreme temperatures can help us appreciate the unique climate of this region and its implications for residents and visitors alike. In this article, we will delve into why Arizona stands out as the hottest state and explore the various aspects that define its climate.
Extreme heat is not just a weather phenomenon; it has far-reaching effects on health, economy, and the environment. The state of Arizona, with its desert landscapes and record-breaking temperatures, serves as a prime example of how climate conditions can shape daily life. From the blistering summer days to the unique adaptations of its flora and fauna, Arizona offers a fascinating case study of heat resilience.
As we explore the factors that make Arizona the hottest state, we will also examine the implications of climate change and how it exacerbates the challenges faced by this region. By understanding the geography, climate patterns, and human adaptations, we can gain valuable insights into managing extreme heat in a rapidly warming world.
Read also:Rebecca From Pawn Stars The Ultimate Guide To Her Life Career And Impact
Overview of the Hottest State in the United States
Arizona is widely recognized as the hottest state in the United States due to its arid desert climate and consistently high temperatures. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Arizona experiences some of the highest average temperatures in the country, particularly during the summer months. The state's location in the Sonoran Desert contributes significantly to its extreme heat.
One of the defining characteristics of Arizona's climate is its low humidity levels. This dry heat can make temperatures feel even more intense, as the body struggles to cool itself through sweat evaporation. Additionally, the state's elevation and geographic features, such as the Grand Canyon and Phoenix metropolitan area, play a role in shaping its unique weather patterns.
Geography and Climate Patterns
The geography of Arizona plays a crucial role in determining its climate. The state is situated in the southwestern United States, bordered by Mexico to the south and Nevada to the west. Its diverse landscapes range from desert lowlands to high-elevation mountain ranges. This variety influences temperature distribution across the state.
- The Sonoran Desert dominates the southern and western regions, contributing to the state's reputation for extreme heat.
- Phoenix, the state capital, holds the record for the most days per year with temperatures exceeding 100°F (38°C).
- Higher elevations, such as Flagstaff, experience cooler temperatures, but the majority of the state remains hot and arid.
Why Arizona is the Hottest State
Several factors contribute to Arizona's status as the hottest state in the United States. These include its desert climate, geographic location, and urban heat island effects. Understanding these elements provides a comprehensive view of why Arizona stands out in terms of temperature.
Desert Climate
The Sonoran Desert, which spans much of Arizona, is one of the hottest deserts in North America. Its low humidity and minimal precipitation create ideal conditions for high temperatures. During the summer, daytime highs often exceed 110°F (43°C) in cities like Phoenix and Tucson.
Urban Heat Island Effect
Cities like Phoenix and Tucson experience an urban heat island effect, where human activities and infrastructure amplify the natural heat of the desert. Asphalt roads, concrete buildings, and reduced vegetation contribute to higher temperatures in urban areas compared to surrounding rural regions.
Read also:Curt Smith Wife A Comprehensive Look Into The Life And Relationship
Temperature Records in Arizona
Arizona holds several temperature records that underscore its reputation as the hottest state. For instance, the city of Lake Havasu recorded a temperature of 128°F (53°C) in 1994, one of the highest temperatures ever measured in the United States. These records highlight the extreme nature of Arizona's climate.
Historical Temperature Trends
Historical data from the NOAA shows that Arizona's temperatures have been rising over the past few decades. This trend is consistent with global climate change patterns, where desert regions are experiencing faster warming compared to other areas. The increase in average temperatures poses significant challenges for both human and ecological systems in the state.
Health Implications of Extreme Heat
Extreme heat poses serious health risks to residents and visitors in Arizona. Heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke, are common during the summer months. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, children, and outdoor workers, are particularly at risk.
- Heatstroke is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
- Dehydration and sunburn are other common issues associated with prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
- Public health initiatives in Arizona focus on educating the population about heat safety and providing cooling centers during heatwaves.
Economic Impact of Extreme Heat
The economic impact of extreme heat in Arizona is significant. The state's agriculture, tourism, and energy sectors are all affected by high temperatures. For example, farmers face challenges in maintaining crop yields under extreme heat conditions, while tourists may avoid visiting during the hottest months.
Energy Demand and Infrastructure
High temperatures lead to increased energy demand for air conditioning, straining the state's power grid. Utilities in Arizona have implemented measures to manage peak electricity usage during heatwaves, but the growing population and rising temperatures continue to pose challenges for energy infrastructure.
Environmental Consequences of Extreme Heat
Extreme heat has profound effects on Arizona's natural environment. Desert ecosystems, which are already adapted to arid conditions, face additional stress from rising temperatures. Wildfires, droughts, and habitat loss are some of the environmental consequences of prolonged heatwaves.
Wildlife Adaptations
Despite the harsh conditions, Arizona's wildlife has developed remarkable adaptations to survive in extreme heat. Animals such as the desert tortoise and Gila monster have evolved strategies to conserve water and avoid the hottest parts of the day. However, climate change threatens to disrupt these delicate balances, endangering native species.
Coping with Extreme Heat in Arizona
Residents of Arizona have developed various strategies to cope with extreme heat. From architectural innovations to community initiatives, these efforts aim to mitigate the impacts of high temperatures on daily life.
- Shade structures and reflective building materials help reduce indoor temperatures.
- Community cooling centers provide relief for those without access to air conditioning.
- Public awareness campaigns educate people about staying safe during heatwaves.
Climate Change and the Future of Arizona's Heat
Climate change is expected to intensify the heat in Arizona, with projections indicating even higher temperatures in the coming decades. Scientists warn that the frequency and severity of heatwaves will increase, posing greater challenges for the state's residents and ecosystems.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the impacts of climate change requires a combination of adaptation and mitigation strategies. Arizona's government and local communities are exploring ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance urban planning, and improve public health infrastructure to better withstand the effects of extreme heat.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Arizona's status as the hottest state in the United States is due to a combination of natural and human factors. Its desert climate, geographic location, and urban heat island effects all contribute to the extreme temperatures experienced in the state. While extreme heat poses significant challenges, the resilience of Arizona's people and ecosystems offers valuable lessons for managing climate change.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with extreme heat in Arizona. By engaging in discussions and exploring related articles, we can deepen our understanding of this critical issue. Together, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future in the face of a warming world.
Table of Contents
- Overview of the Hottest State in the United States
- Why Arizona is the Hottest State
- Temperature Records in Arizona
- Health Implications of Extreme Heat
- Economic Impact of Extreme Heat
- Environmental Consequences of Extreme Heat
- Coping with Extreme Heat in Arizona
- Climate Change and the Future of Arizona's Heat
- Conclusion